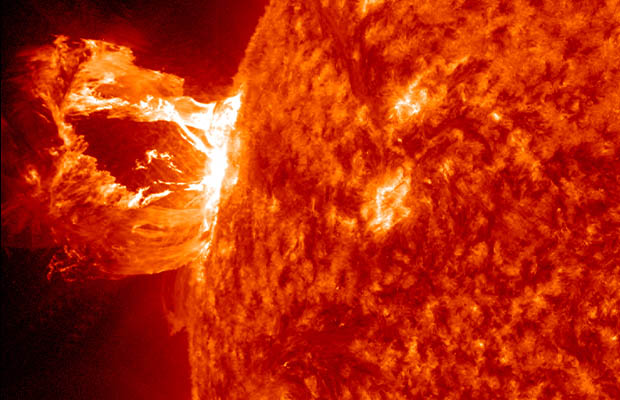
Do you know what is a solar storm? Generally speaking, the term “solar storm” describes when an intense eruption of energy from the sun shoots into space and interacts with Earth. Do you want to learn more about this solar phenomenon? You belong in this post.
When a solar storm strikes the Earth, it often produces a dazzling “northern lights” display in parts of the atmosphere that can be seen in areas close to the Satellites and other types of electronic communication can be affected by solar storms, which can also occur in the Arctic Circle.
Learn more by continuing to read!
Table of Contents
What Are Solar Storms?
When certain events take place on the Sun’s surface, the atmosphere on Earth is affected in a way that is visible to us as a solar storm.
Large energy bursts from the Sun, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, can cause solar storms. These events swiftly direct a stream of electrical charges and magnetic fields toward Earth.
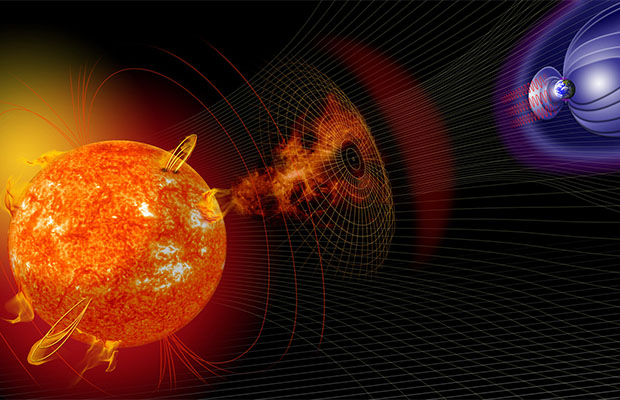
One of the effects of a solar storm striking Earth is the creation of the “northern lights” which are seen in the regions around the Satellite and other electronic communications are disrupted by solar storms, which is a negative consequence. Arctic Circle.
Read More: What is the Center of Our Solar System?
Types of Solar Storms
Solar Storms come in the form of the following types:
- Solar Flares: A solar flare is a brief increase in brightness that occurs suddenly on the Sun. It is typically seen close to the surface or near a group of sunspots. A coronal mass ejection frequently, but not always, occurs along with strong flares. Even the most powerful flares are barely detectable in the total solar irradiance (the “solar constant”).
- Coronal Mass Ejection: A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant discharge of plasma from the solar corona along with an auxiliary magnetic field. They typically exist during an eruption of a solar prominence and frequently follow solar flares.
- Geomagnetic Storm: A geomagnetic storm, also known as a solar storm, is a brief disruption of the Earth’s magnetosphere brought on by an interaction between the magnetic fields of the Sun and the Earth.
- Solar Particle Events: A solar particle event, also known as a solar proton event (SPE), or prompt proton event, happens when solar particles, most of which are protons, are accelerated either by coronal mass ejection shocks in interplanetary space or by flares that occur close to the Sun.
Effects of Solar Storms on Earth
Solar Storms can have the following effects on Earth:
- Humans and other mammals are susceptible to radiation poisoning from very high-energy particles, such as those carried by coronal mass ejections.
- The magnetic field of the Earth is momentarily perturbed when a coronal mass ejection collides with the atmosphere.
- Many urban centers are at risk because it has the ability to veer satellites off course and make them fall to the earth’s surface.
- Animals that migrate and use magneto reception to navigate, like birds and bees, have been the subject of some scientific speculation.
- Geomagnetically induced currents can be created in pipelines by rapidly fluctuating geomagnetic fields. For pipeline engineers, this can result in a variety of issues. Erroneous flow information from pipeline flow meters can cause the pipeline to corrode much more quickly.
How to Forecast Space Weather?
Space weather forecasting differs slightly from forecasting on the ground. The main distinction is that meteorologists on Earth have access to millions of measurements that they can collect and include in their forecasting models. There are only a few locations in space where scientists can deploy instruments to monitor solar activity, according to Woodroffe.
“We don’t have a great picture of what happens between the sun and the Earth,” he explains. “Because satellites in orbit move, there aren’t many places where you can set up a dependable asset and just leave it there.” Lagrange points are uncommon locations where a satellite is held in place by the gravitational pull of both the Earth and the sun at the same time. That’s where NASA has placed their “most vital space weather monitors,” Including a partnership with the European Space Agency (ESA), according to Woodroffe. By the end of this decade, the Vigil mission, being developed by the ESA, will send a spacecraft to a Lagrange point close to the sun. While orbiting Earth, NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory investigates the sun.
According to Woodroffe, scientists use their cameras and sensors to keep an eye on the sun in case the brightness emanating from its surface changes. Only a few frames or even a few seconds may pass during which a brightness surge is visible.
FAQs About Solar Storms
How Dangerous Are Solar Storms?
While the geomagnetic waves produced by solar storms are invisible and safe for everyone on Earth’s surface, they have the power to disrupt power grids, impede radio communications, expose airline crews to dangerous radiation levels, and deviate important satellites from their course.
What Effect Do Solar Storms Have on Living Beings on Earth?
Fortunately, flares never significantly affect Earth, no matter what happens. The atmosphere of the Earth essentially serves as a shield to keep cosmic radiation from reaching the surface. At ground level, there may be measurable effects, but the radiation exposure is quite minimal.
When Was the Last Solar Storm?
At 4:25 pm, the Sun produced a powerful solar flare. EDT on Oct. 2, 2022.





